Skin Cancer and Outdoor Work: Do You Know the Risks?
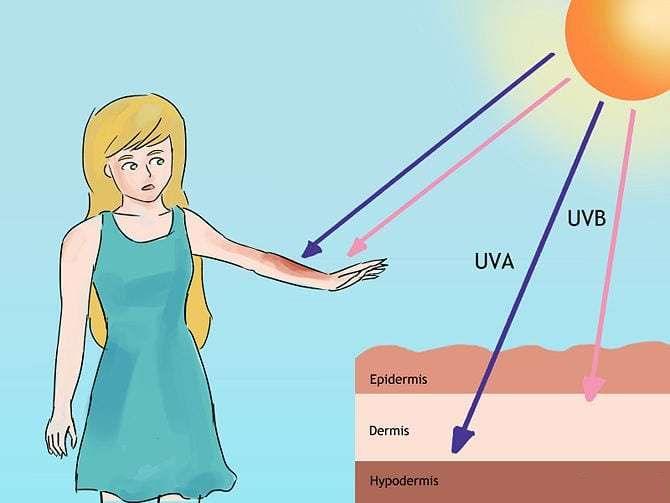
Sun exposure causes most skin cancer. The exposure may be long term or short term - where there are periods of intense sun exposure, causing burns. UV light in sunlight damages the DNA in the skin cells, and over time, this damage can lead to skin cancer.
If your employees work outside in hot weather, then you should put measures in place to reduce their sun exposure. One in four skin cancer deaths results from those who work in construction or farming and are exposed to harmful sun rays.
Once you damage your skin, it is permanent. The only way you can protect your workers from harm is to limit their exposure. Also, you can provide sun cream, protective clothing, allow frequent breaks, and put other measures in place to protect your workers.
Skin cancer is linked to the sun. Both you and your employees need to be informed about how to reduce risks. Those who work outside, such as construction and agricultural workers, need to be trained on how to protect their skin. Find out how you can protect your workers.
- Page Contents
- What is Skin Cancer?
- Who is at Risk of Skin Cancer?
- What are the Symptoms of Skin Cancer?
- Conditions which Increase Your Risk
- How can I Protect my Workers?
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is a growth that is uncontrolled or a replication of abnormal skin cells. Exposure to UV radiation from the sun light or tanning beds can cause it. When this exposure triggers mutations or genetic defects, it damages you DNA. As a result, your skin cells multiply rapidly, which then form malignant tumours.
Who is at Risk of Skin Cancer?
Anyone who is exposed to sun for a long time is at risk. Some of the main jobs are farmers, landscapers, and gardeners. A suntan is your body’s natural dense against the sun. It helps to protect you from burns. However, there is a fine line between a tan and a burn. Your skin reacts like an allergic reaction to the sun which causes a burn. Also, it sometimes causes unseen damage to your DNA and skin cells.
Those who are older have a higher likelihood of developing skin cancer, but it can occur in young people too. Often workers are cavalier about sun protection and also assume that the UK's cloud cover protects them from harm, but that is not the case at all. You still need sun cream on a cloudy day.
What are the Symptoms of Skin Cancer?
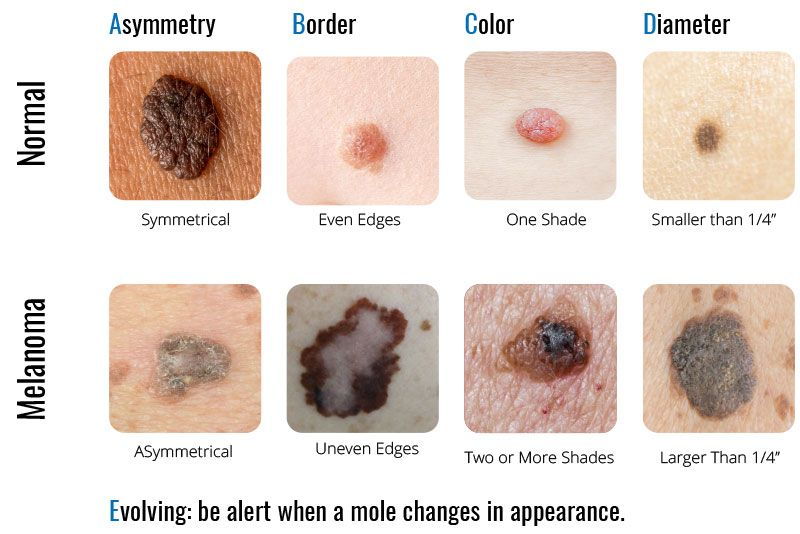
Any changes to moles, freckles, or your skin could be signs of skin cancer. Make sure you check your skin regularly for any changes. If you see a new sore or growth that is not healing; a spot, mole, or sore that hurts and itches; or a mole or growth that bleeds, crusts over, or scabs, then consult your doctors because these are also signs.
Here are some photographic examples of melanoma skin cancer. It is important to note that not all skin cancers will look like these examples.
Conditions which Increase Your Risk
- Weakened immune systems
- Gender (men are two times more likely to develop skin cancer)
- Skin tone (those with lighter skin tones, those with blonde or red hair, blue or green eyes, skin that burns easily, or freckles are more likely)
- Having a large number of moles
- Family history
- Inherited conditions
- Smoking
- Chemical exposure (arsenic, industrial tar, coal, paraffin, some oils)
- Outdoor workers (or outdoor leisure/activity seekers)
- Tanning bed users
How can I Protect my Workers?
2% of all skin cancer cases are from outdoor workers, and of that 2%, 44% of those workers work in the construction industry with another 22% of deaths in farmers. It is vital you keep your workers safe and understand the risks.
These following measures will help you protect your workers:
- Wear sun protective clothing, long sleeves, closely woven knits, long trousers.
- Avoid light, see-through clothing.
- Shorts to the knee offer more protection than shorter shorts.
- Collars to protect the back of the neck.
- Hats with a 3 inch wide brim to keep the sun off the face, neck, and ears - protect bald spots.
- Hardhats can have a flap or extra brim fitted.
- Wear sunglasses or safety glasses that filter UV rays.
- Sunscreen that has at least SPF 15 and is water-resistant.
- Apply sunscreen every two hours or more often if sweating.
- UV rays reflect off water, sand, concrete, light surfaces, and snow - take extra care when working near these areas.
- Allow workers to rest in the shade or erect a temporary shelter.
- Reorganise tasks to be done early morning before 10 am or after 4 pm when possible to avoid the greatest sun intensity.
Conclusion
It is important for you to know how to protect yourself and your workers from the sun. Firstly, you need to understand what skin cancer is, who is at risk, and the symptoms. By understanding these, you can better protect your workers from harm and lower their chance of developing skin cancer.