Spill Kits and Spillage Response in Industrial Workplaces - The Ultimate Guide
Safety is paramount in the dynamic and often hazardous environment of industrial workplaces. A critical aspect of workplace safety that often goes unnoticed until an emergency arises is the management of spills. Whether dealing with oils, chemicals, or other hazardous substances, having an effective spill response plan is crucial. This is where spill kits come into play.
This guide will explore the importance of spill kits, their components, and best practices for spill response in industrial settings.

Understanding Spill Kits: The Essentials
What is a Spill Kit?
A spill kit is a collection of materials and tools designed to clean up and manage the spillage of various substances safely and efficiently. These kits are vital in minimising the impact of spills on health, safety, and the environment.
Spill kits vary in size and content and are tailored to the specific substances and volumes commonly encountered in the workplace.
Why Are Spill Kits Important?
Spill kits are essential for several reasons:
- Safety: They help protect employees from exposure to hazardous substances, reducing the risk of injury or illness.
- Environmental Protection: Proper spill response minimises environmental contamination, preserving ecosystems and complying with environmental regulations.
- Cost Savings: Effective spill management prevents damage to property and reduces cleanup costs and potential fines.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are legally required to have spill response measures in place.
About Those Legal Requirements...
The UK's Health & Safety Executive outlines requirements for the control and safe management of hazardous substances, including the necessity of having spill response plans and kits in workplaces.
The Environmental Protection Act 1990 requires businesses in the UK to prevent environmental contamination and outlines the duty of care regarding waste management, which includes measures for spill prevention and response.
The Control of Major Accident Hazards (COMAH) Regulations apply to businesses that handle dangerous substances. These regulations require facilities to have emergency plans and spill response strategies to manage potential accidents.
Spill Kit Colour Coding
To ensure an efficient and appropriate response to the various types of spillage, spill kits are colour coded to help identify their specific uses.
- White spill kits are designed for "Oil Only" applications and are ideal for absorbing oil-based liquids while repelling water. Useful in marine environments or areas with oil and water mixtures.
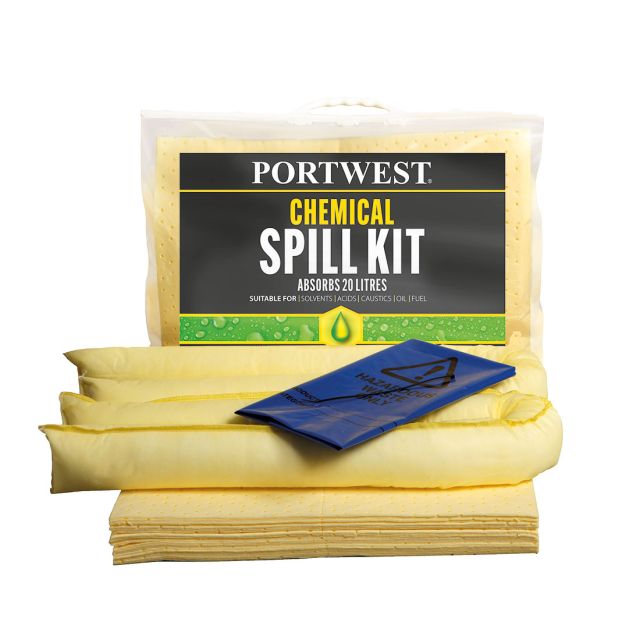
- Yellow spill kits are designated for chemical spills. They contain absorbents that can safely handle hazardous substances and help contain and neutralise dangerous chemicals.
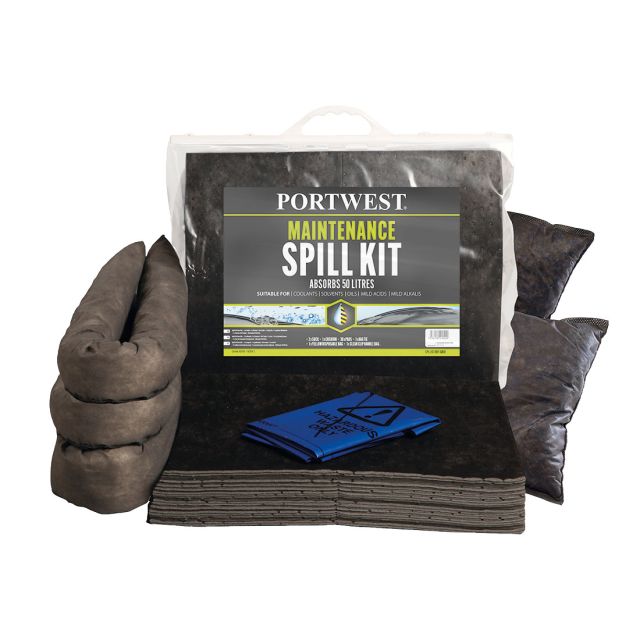
- Black spill kits, also known as "Maintenance" kits, are versatile and can be used for general-purpose spills such as non-aggressive liquids, including oils, coolants, solvents, and water-based fluids.
This colour-coding system simplifies the selection and deployment of spill kits in diverse industrial and commercial settings.
Components of Spill Kits
Absorbents
Absorbents are materials that soak up liquids. They come in various forms, including pads, rolls, socks, and granules, each suited to different types of spills and surfaces. Absorbents are categorised based on the type of substance they can handle:
- Universal Absorbents: Suitable for water-based fluids, oils, and chemicals.
- Oil-Only Absorbents: Designed specifically for oil and hydrocarbon spills, repelling water.
- Chemical Absorbents: Made for aggressive chemicals, including acids and bases.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE is crucial for protecting workers during spill response. Common PPE in spill kits includes gloves, goggles and/or face shields, and protective overalls. The level of protection required depends on the nature of the hazardous material involved.
If your spill kit does not contain these PPE items, you should provide them alongside the kit.
Spill Containment and Cleanup Tools
These tools help contain and clean up spills safely and efficiently:
- Containment Booms: Prevent the spread of liquid spills, particularly in water bodies.
- Drain Covers: Block drains to prevent contaminants from entering water systems.
- Spill Pads, Socks and Pillows: Absorb liquids quickly, ideal for smaller spills.
- Disposal Bags: Ensure safe disposal of used absorbents and contaminated materials.
Emergency Spill Response Equipment
Some spill kits include equipment for larger or more hazardous spills, such as:
- Neutralising Agents: Used for acid or base spills to render the substances less harmful.
- Fire Extinguishers: In case of flammable liquid spills, especially in areas where fires are a risk.
- First Aid Supplies: To treat injuries that may occur during spill response.
Implementing an Effective Spill Response Plan
Assessing the Risk
Before establishing a spill response plan, it's crucial to assess the types of substances present in the workplace and the potential risks they pose.
This assessment should consider:
- Quantity and Types of Substances: Understanding the specific hazards associated with each substance.
- Spill Scenarios: Identifying likely spill scenarios and their potential impact.
- Regulatory Requirements: Ensuring compliance with relevant health, safety, and environmental regulations.
Spill Kit Placement and Accessibility
Spill kits should be strategically placed throughout the workplace, particularly in areas where spills are most likely to occur, such as near storage areas for hazardous materials. They should be easily accessible to all employees, and their locations should be clearly marked.
Training and Drills
Training is a critical component of an effective spill response plan. Employees should be trained in:
- Recognising Different Types of Spills: Knowing how to identify and classify spills quickly.
- Using Spill Kits and PPE: Proper usage and disposal of kit contents and personal protective equipment.
- Emergency Procedures: Including evacuation routes, communication protocols, and first aid.
- Regular drills and refresher training sessions help keep employees prepared and confident in handling spills.
Response Procedures
Having clear, well-documented spill response procedures is essential. These procedures should include:
- Immediate Actions: Steps to take immediately following a spill, such as alerting supervisors, using containment measures, and isolating the area.
- Spill Assessment: Determining the nature and extent of the spill, including potential hazards.
- Containment and Cleanup: Using the appropriate tools and materials to contain and clean up the spill safely.
- Waste Disposal: Ensuring that all contaminated materials are disposed of according to regulations.
- Incident Reporting: Documenting the spill and the response actions taken, including any injuries or environmental impacts.
Maintaining and Updating Spill Kits
Regular Inspections
Spill kits should be inspected regularly to ensure they are complete and in good condition. Checklists can help track the contents and expiration dates of items in the kit.
Replenishment and Upgrades
After any spill response, used items in the kit should be replenished immediately. Additionally, spill kits should be updated periodically to reflect changes in the types of substances handled in the workplace or advancements in spill response technology.
Continuous Improvement
Post-incident reviews and feedback from employees can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the spill response plan and areas for improvement. Regularly updating training programs and procedures based on these insights helps maintain a high level of preparedness.
Conclusion: Prioritising Safety with Spill Kits
Spill kits are a vital component of a comprehensive safety strategy in industrial workplaces. They provide the tools and materials necessary to respond to spills quickly and effectively, protecting employees, the environment, and company assets. By understanding the components of spill kits, implementing robust spill response plans, and maintaining readiness through training and regular kit inspections, businesses can significantly reduce the risks associated with hazardous material spills.
Investing in high-quality spill kits and ongoing safety training not only ensures regulatory compliance but also fosters a culture of safety and responsibility among employees. In the event of a spill, a well-prepared response can make all the difference, mitigating potential damage and ensuring a swift return to normal operations.