Celebrating 50 Years of the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974: A Milestone for the UK Workforce
As we approach the 50th anniversary of the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 (HSWA) on 31st July 2024, it is a good time to reflect on the profound impact this landmark legislation has had on the UK workforce.
Introduced at a time when workplace safety was far from guaranteed, the HSWA has transformed the working environment across various sectors, fostering a culture of safety and well-being that continues to evolve.

This article explores the origins, benefits, and enduring legacy of the HSWA, emphasising its critical role in protecting and empowering workers in the UK.
- Page Contents
- In the beginning
- Key Provisions of the HSWA
- Benefits of the HSWA
- The Role of the HSE
- Industry Impacts
- Evolution of Safety Culture
- Future Challenges and Opportunities
- Conclusion
The Genesis of the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974
Before the the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974, workplace safety regulations in the UK were fragmented and inadequate. Various industries had their own set of rules, resulting in inconsistencies and gaps in protection.

The need for comprehensive legislation became increasingly apparent as industrial accidents and occupational diseases highlighted the severe consequences of insufficient safety measures.
The HSWA was introduced to address these issues comprehensively. Spearheaded by the Committee on Safety and Health at Work, chaired by Lord Robens, the Act aimed to consolidate and extend existing safety laws, creating a unified framework for managing workplace health and safety.
The Act's primary objective was to "secure the health, safety, and welfare of persons at work," marking a significant shift towards a proactive approach to occupational safety.
Key Provisions of the HSWA
The HSWA established several fundamental principles that continue to underpin workplace safety regulations today:
- General Duties of Employers and Employees: The Act places a legal obligation on employers to ensure, as far as reasonably practicable, the health, safety, and welfare of their employees. This includes providing safe equipment, adequate training, and a safe working environment. Employees, in turn, are required to take reasonable care for their own health and safety and that of others who may be affected by their actions.
- The Health and Safety Executive (HSE): The Act led to the creation of the Health and Safety Executive, an independent regulator responsible for enforcing workplace health and safety laws. The HSE provides guidance, conducts inspections, and has the authority to prosecute organisations and individuals for breaches of safety regulations.
- Risk Assessments and Safety Policies: Employers are required to conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential hazards and implement measures to mitigate them. Additionally, organisations with five or more employees must have a written health and safety policy outlining their approach to managing workplace risks.
- Consultation with Employees: The Act encourages employers to consult with employees or their representatives on health and safety matters. This collaborative approach ensures that workers have a voice in the decisions that affect their well-being.
Benefits of the HSWA to the UK Workforce
The HSWA has had a transformative impact on the UK workforce, providing numerous benefits that have enhanced the safety, health, and overall quality of working life for millions of employees.
Reduction in Workplace Accidents and Illnesses
One of the most significant achievements of the HSWA is the substantial reduction in workplace accidents and occupational illnesses. The introduction of systematic risk assessments, coupled with stringent safety protocols, has led to safer working conditions across industries.
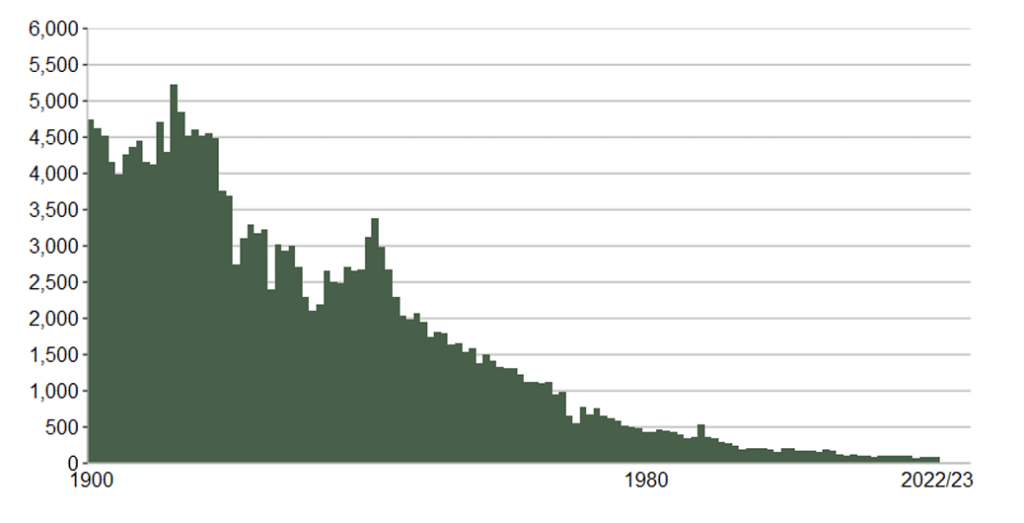
According to HSE statistics, fatal injuries in the workplace have decreased dramatically since the Act's implementation, highlighting its effectiveness in preventing accidents.
Enhanced Employee Well-being
The HSWA's emphasis on a safe working environment extends beyond physical safety to encompass overall employee well-being. By mandating ergonomic assessments, mental health considerations, and stress management programs, the Act has contributed to a more holistic approach to worker health.
This focus on well-being has been linked to increased job satisfaction, higher productivity, and reduced absenteeism.
Legal Protection and Empowerment
The HSWA provides a robust legal framework that empowers employees to demand safe working conditions. Workers have the right to refuse work that poses a serious risk to their health and safety without fear of retaliation.
This legal protection has fostered a culture where safety concerns are taken seriously, and employers are held accountable for maintaining safe workplaces.
The Role of the Health and Safety Executive (HSE)
The HSE has played a pivotal role in the successful implementation and enforcement of the HSWA. As an independent regulator, the HSE conducts inspections, investigates accidents, and provides guidance to ensure compliance with safety regulations.

The HSE's proactive approach includes the development of industry-specific safety standards and the promotion of best practices.
Inspections and Enforcement
Regular inspections by the HSE have been instrumental in identifying and rectifying safety violations. These inspections are not merely punitive; they serve as educational opportunities for organisations to improve their safety protocols.
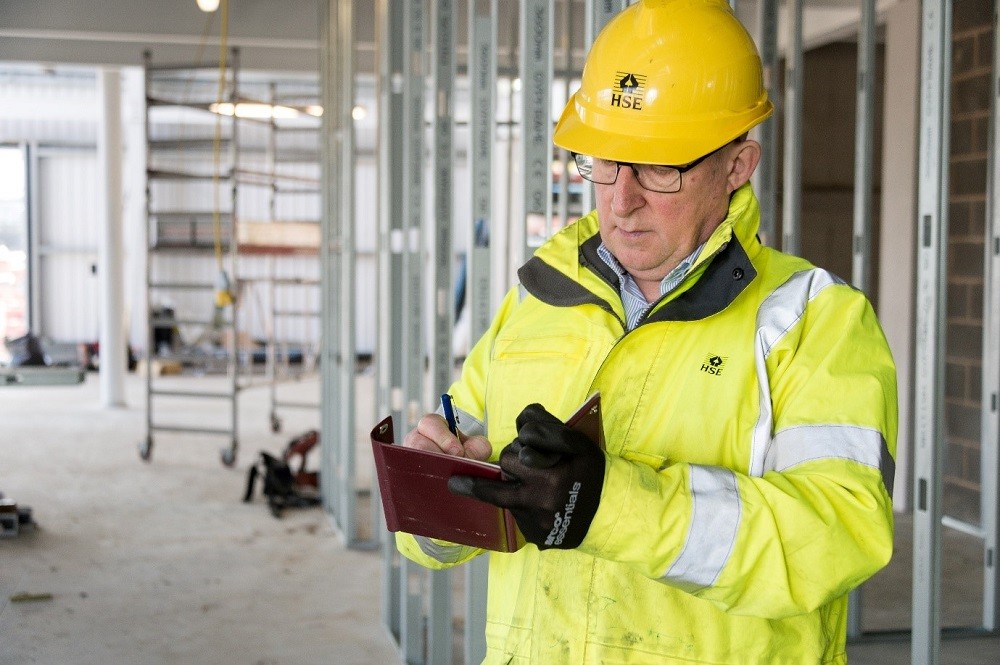

The HSE's enforcement actions, including prosecutions and fines, act as a deterrent against non-compliance, reinforcing the importance of adhering to safety standards.
Guidance and Support
The HSE provides a wealth of resources to help employers and employees understand their responsibilities under the HSWA.
This includes detailed guidance documents, case studies, and online tools designed to assist in the development and implementation of effective safety management systems.
The HSE’s support has been invaluable in promoting a culture of safety and ensuring that organisations of all sizes can comply with their legal obligations.
Industry-Specific Impacts
Different industries have unique safety challenges, and the HSWA has been flexible enough to address these varied needs.
Let’s explore how the Act has specifically benefited several key sectors.
Construction
The construction industry is historically one of the most hazardous sectors. Prior to the HSWA, construction workers faced significant risks due to a lack of standardised safety practices.
The HSWA introduced mandatory risk assessments, safety training, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), significantly reducing the number of fatal and serious injuries on construction sites.
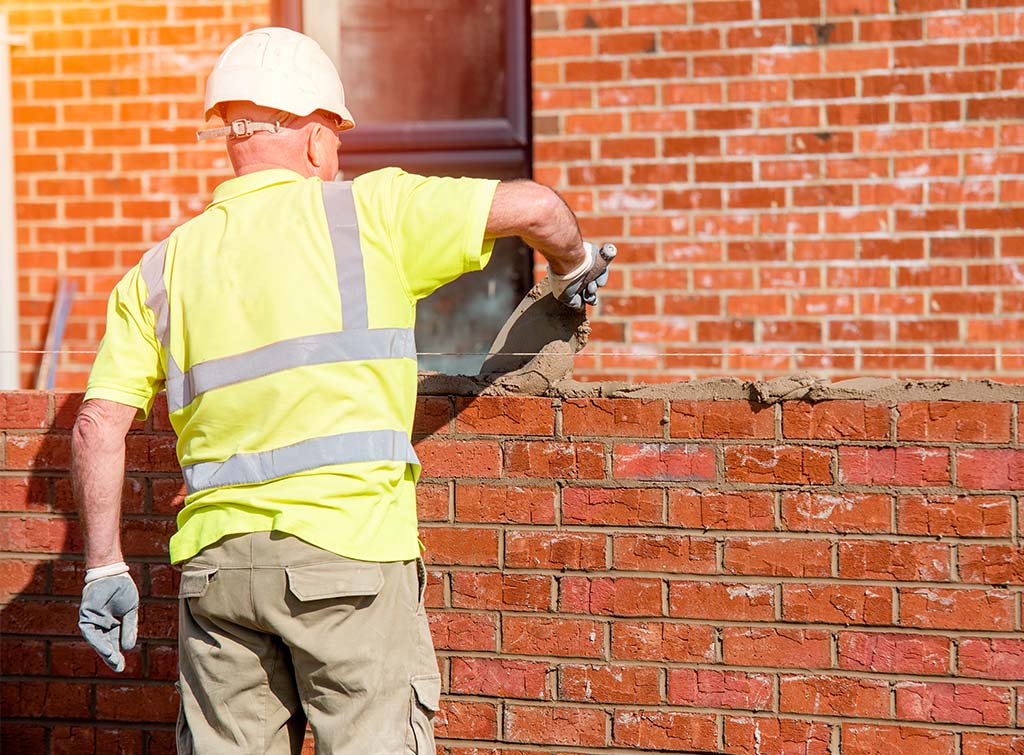

The establishment of the Construction (Design and Management) Regulations under the HSWA has further enhanced safety by ensuring that safety considerations are integrated into the planning and design stages of construction projects.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, the HSWA has driven the adoption of safer machinery, better training programs, and improved operational procedures.
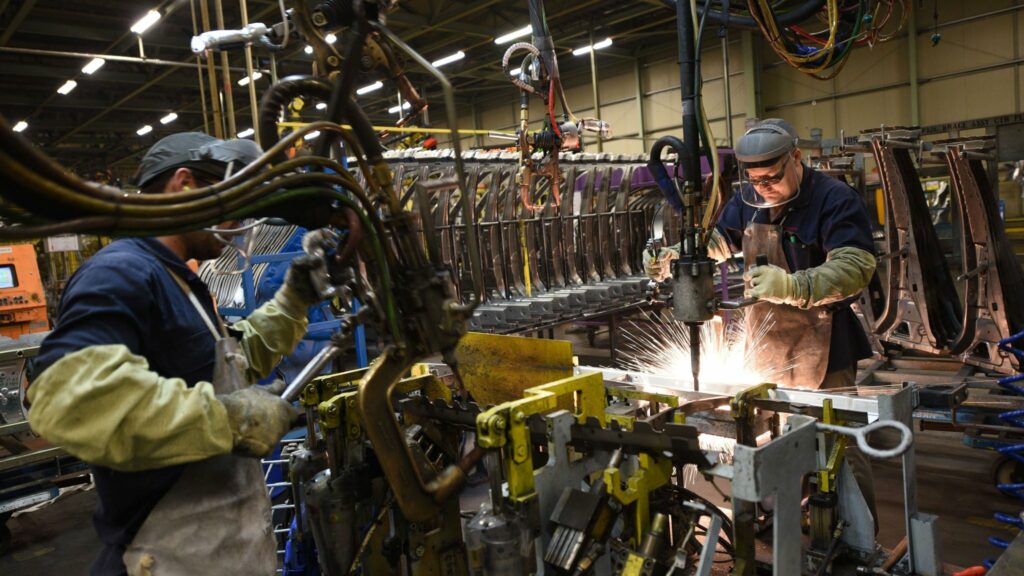

The introduction of safety audits and regular equipment maintenance checks has minimised the risk of accidents caused by machinery malfunctions. Additionally, the emphasis on hazard communication and chemical safety has protected workers from exposure to harmful substances.
Healthcare
Healthcare workers face unique risks, including exposure to infectious diseases and physical strain from patient handling. The HSWA has led to the implementation of rigorous infection control protocols, safer patient handling techniques, and the use of ergonomic equipment.
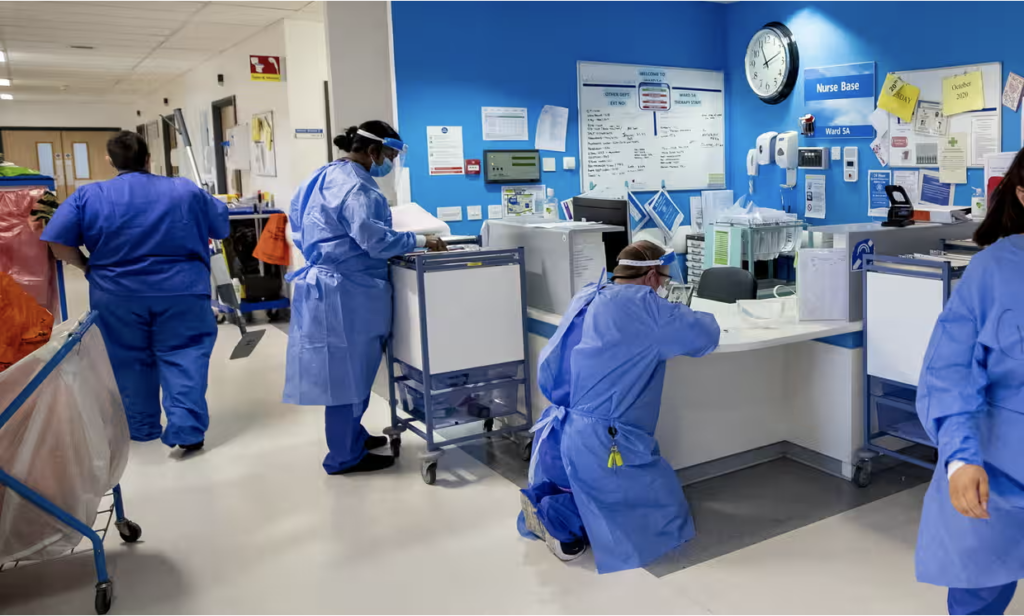

These measures have not only improved the safety of healthcare workers but also enhanced patient care by ensuring that healthcare environments are safer and more efficient.
Agriculture
Agriculture is another sector where the HSWA has had a profound impact. The introduction of safety standards for the use of machinery, pesticides, and other hazardous substances has made farming significantly safer.
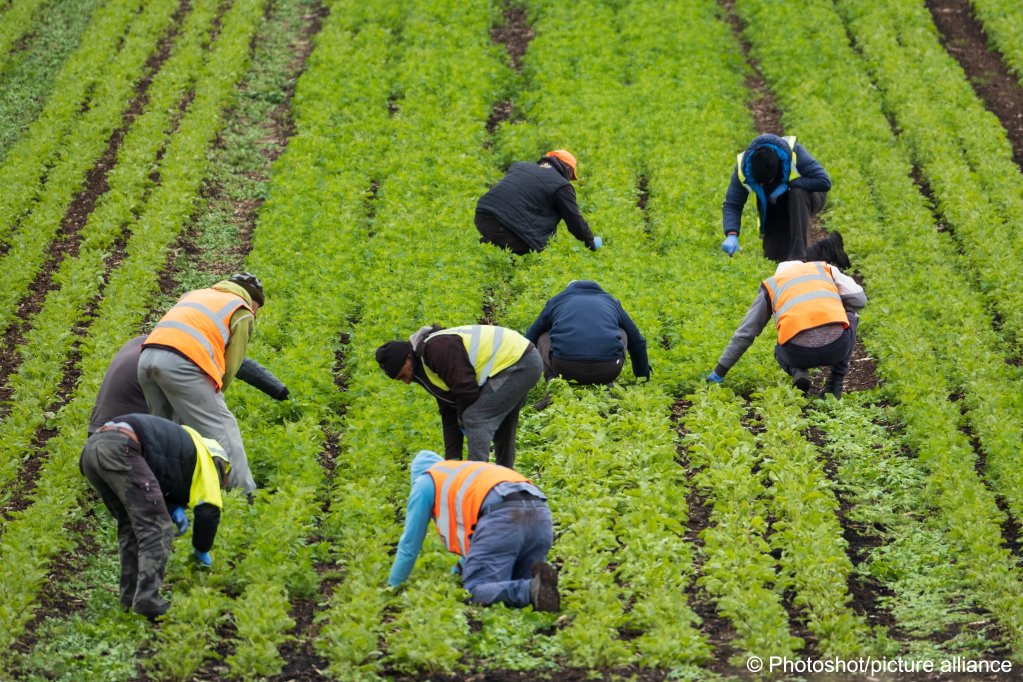

The Act’s requirements for training and protective equipment have helped reduce the high rates of accidents and injuries that once plagued the agricultural sector.
The Evolution of Workplace Safety Culture
The HSWA has been instrumental in fostering a culture of safety that extends beyond mere compliance with regulations. It has encouraged a shift towards proactive risk management and continuous improvement in safety practices.
From Compliance to Proactive Safety Management
Initially, the focus of the HSWA was on ensuring compliance with minimum safety standards. Over the years, however, there has been a significant shift towards proactive safety management.
Organisations are now encouraged to go beyond compliance, identifying potential hazards before they lead to accidents and continuously improving their safety protocols.

This proactive approach has been facilitated by advancements in technology, such as the use of predictive analytics and real-time monitoring systems.
Employee Involvement and Safety Leadership
The HSWA has emphasised the importance of involving employees in safety initiatives. This collaborative approach has led to the development of safety committees and the appointment of safety representatives who play a crucial role in identifying hazards and promoting safe practices.
Moreover, the concept of safety leadership has gained prominence, with senior management taking an active role in championing safety and setting a positive example for the entire organisation.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
As we celebrate the 50th anniversary of the HSWA, it is important to recognise the evolving landscape of workplace health and safety and the new challenges that lie ahead.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, including automation, artificial intelligence, and wearable technology, offer new opportunities to enhance workplace safety.
These technologies can help identify hazards more quickly, monitor working conditions in real-time, and provide data-driven insights to improve safety protocols.
However, they also introduce new risks, such as cybersecurity threats and the need for workers to adapt to new systems.
Mental Health and Well-being
In recent years, there has been growing recognition of the importance of mental health and well-being in the workplace.
The HSWA’s framework is increasingly being applied to address issues such as workplace stress, anxiety, and depression.
Employers are encouraged to implement mental health support programs, provide training on mental health awareness, and create a supportive work environment that promotes overall well-being.
Globalisation and Supply Chain Safety
Globalisation has expanded the reach of UK businesses, creating new challenges in ensuring consistent safety standards across international supply chains.

The principles of the HSWA are being extended to address the safety and health of workers in global supply chains, emphasising the need for ethical sourcing and the protection of workers’ rights worldwide.
Conclusion
As the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 reaches its 50th anniversary, its impact on the UK workforce is undeniable.
The Act has transformed workplace safety, significantly reducing accidents and illnesses, enhancing employee well-being, and fostering a culture of proactive safety management.
The establishment of the Health and Safety Executive and the development of industry-specific regulations have further strengthened the framework for protecting workers.
Looking ahead, the HSWA continues to provide a robust foundation for addressing emerging challenges and opportunities in workplace health and safety
As technology advances and the understanding of well-being evolves, the principles of the HSWA will remain essential in ensuring that the UK workforce is protected, empowered, and able to thrive in a safe and healthy environment.
This anniversary is not just a celebration of past achievements but a commitment to ongoing improvement and innovation in the pursuit of safer workplaces for all.